Pauline 1238 (Talk | contribs) |
Pauline 1238 (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
| − | <p>  The approach that we took to use 5% HA is because jejunum intestinal juice has 0.2 to 5% | + | <p>  The approach that we took to use 5% HA is because jejunum intestinal juice has 0.2 to 5% mucin(MUC2)<sup>[<a href="#ref4">4</a>]</sup>, and HA was used because of its same sticky characteristic with mucin and due to its low availability. Our experiment result shows that the microfluidic channel with a complex structure such as channel w/ CF+2villi that includes additional HA is the most suitable for simulating the human intestine.</p> |
</section> | </section> | ||
<!--divider--> | <!--divider--> | ||
Revision as of 11:24, 21 October 2021

Overview
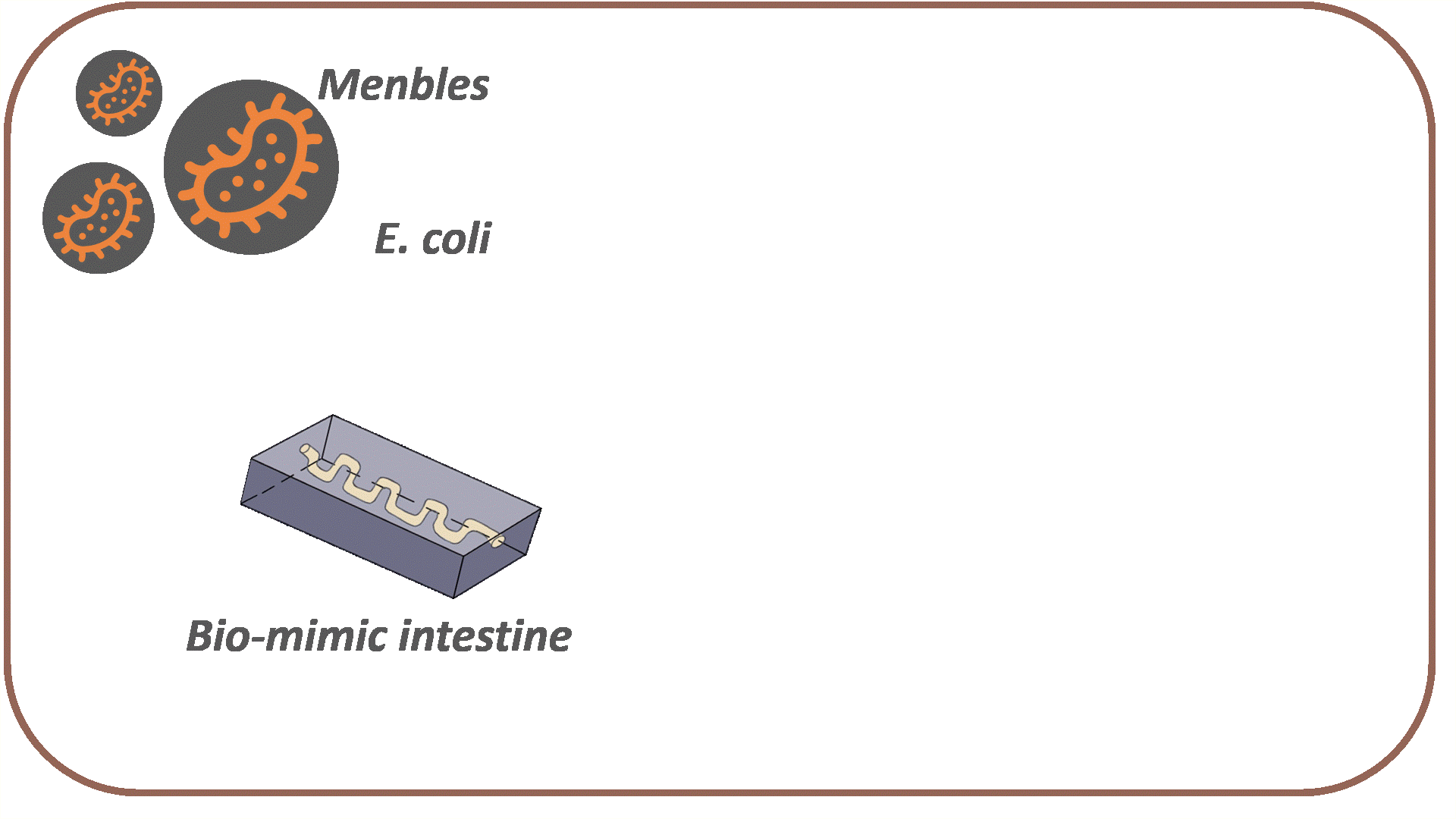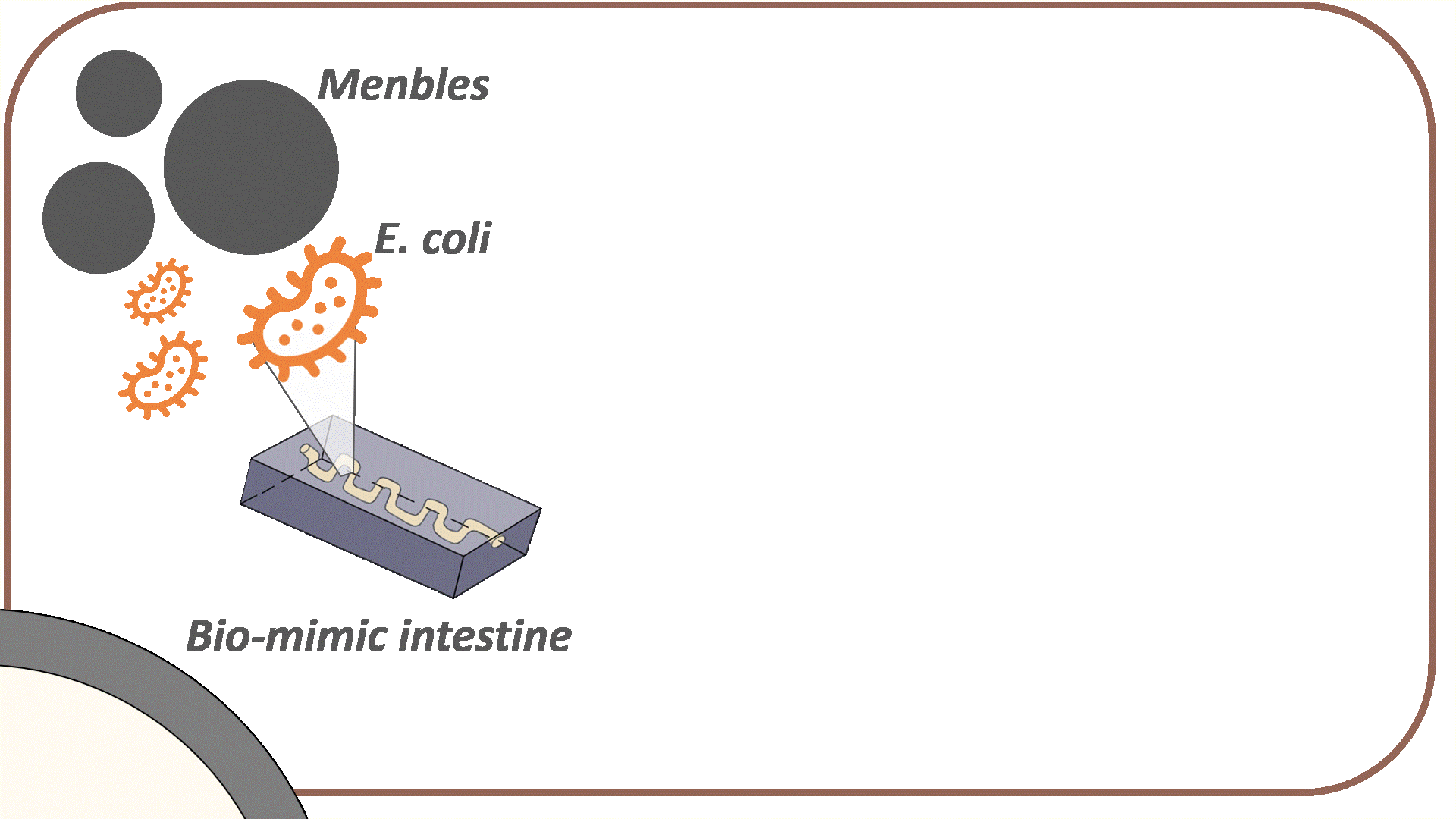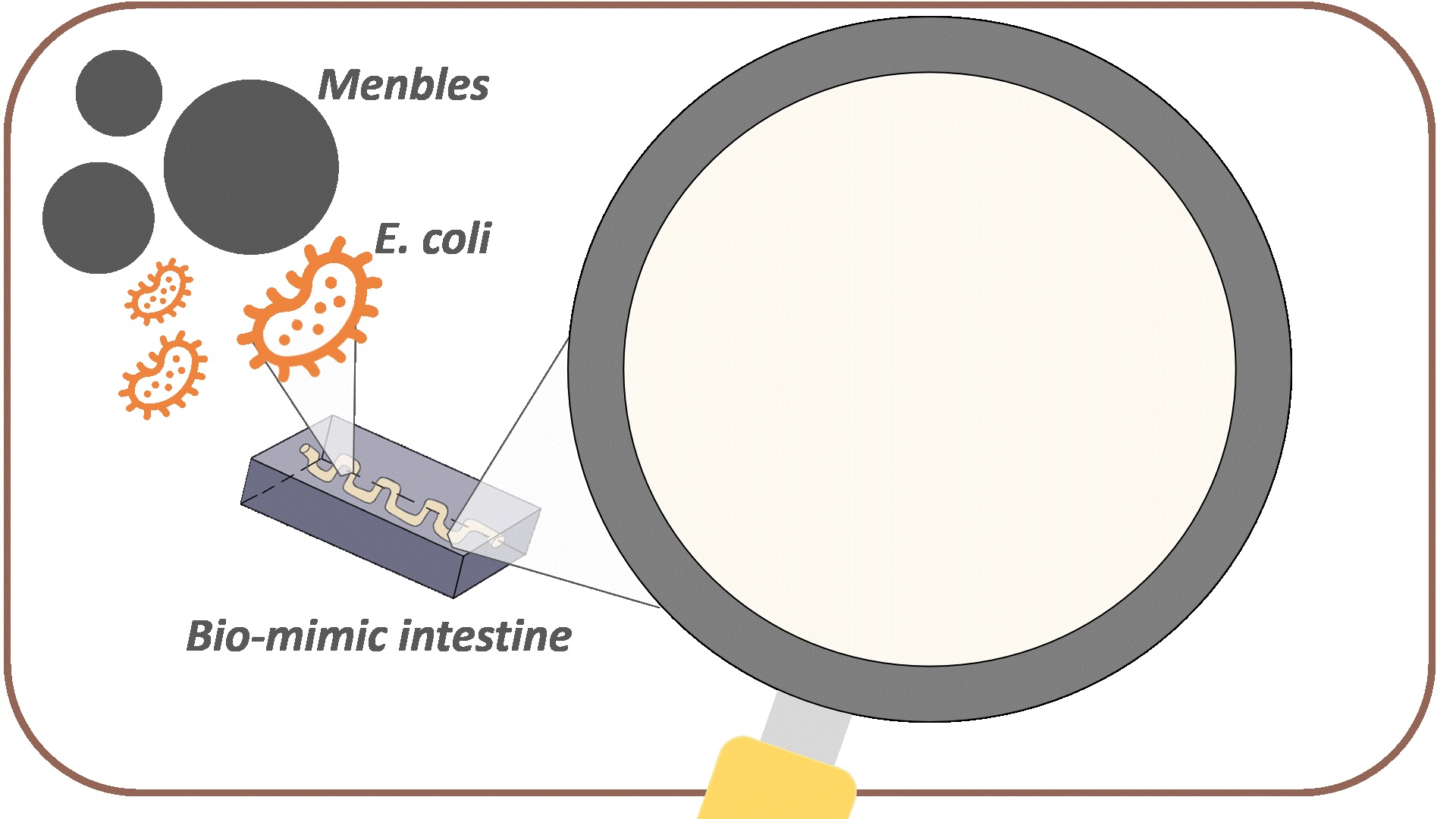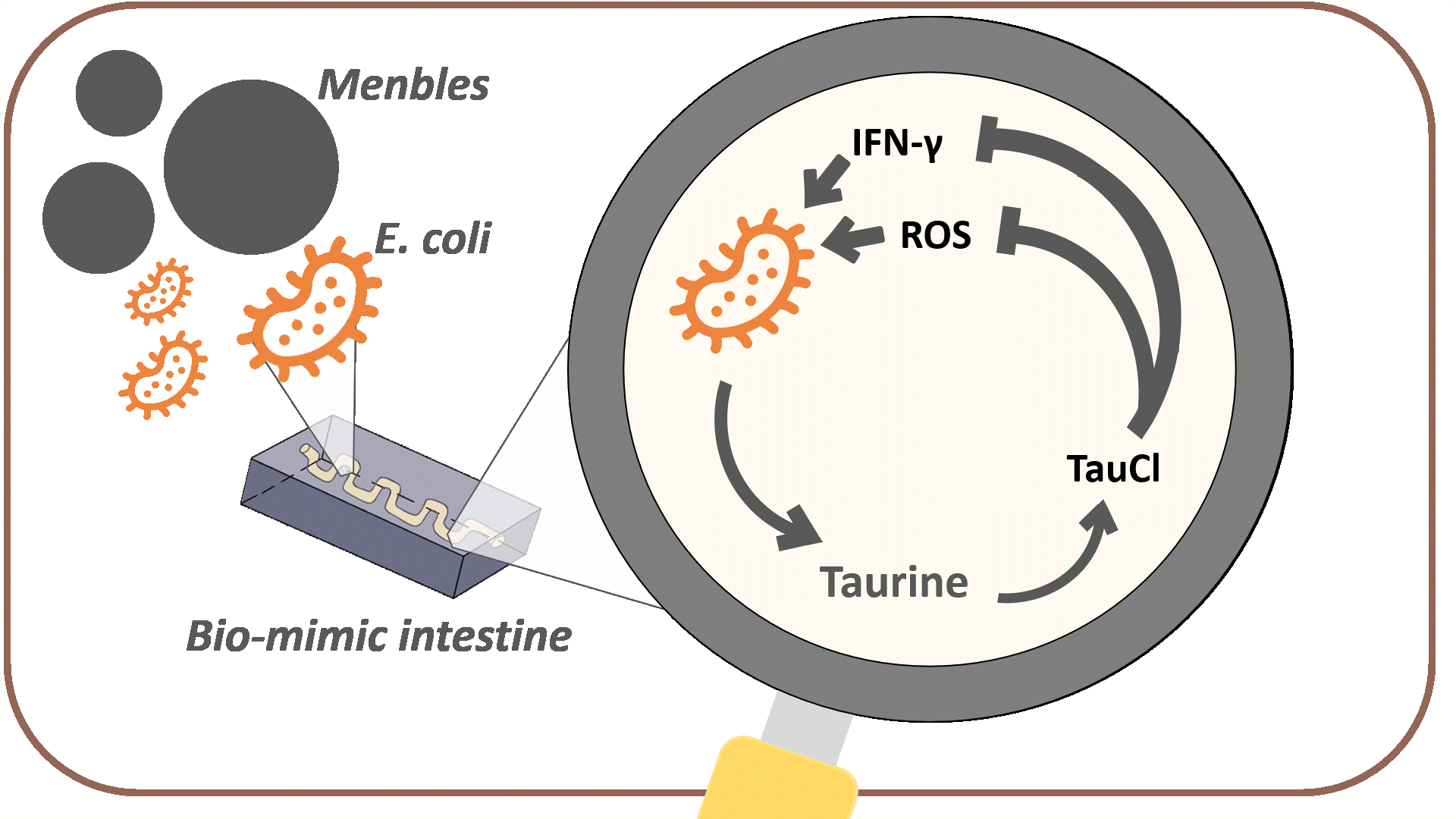
The overall goal of MenTAUR is to relieve depressive symptoms by increasing taurine levels in the intestine. To achieve this, we developed multiple models and conducted wet-lab experiments to prove that our bubble, Menbles, can effectively function and release taurine in the human intestine. Menbles are designed to withstand the acidic environment of the stomach, protecting our encapsulated bioengineered E. coli. We developed a microfluidic chip, f(int), that simulated the intestinal environment, allowing us to determine the retention of E. coli in the jejunum. After confirming that most of our E. coli can adhere to the intestinal walls, we proved that the E. coli could detect stress biomarkers reactive oxygen species (ROS) and IFN-γ through the oxidative stress and IFN-γ sensing systems and produce the taurine production enzymes. Finally, with math-based calculations, we can model the mechanism through which taurine converts into TauCl and reduces ROS and IFN-γ levels in the body, relieving depressive symptoms through the gut-brain axis.
Bubble Production
Menbles are special edible bubbles that serve as a unique depression medication due to its form of coming with a very popular drink all around the world, bubble milk tea. Our depression medication is designed to be incorporated into everyone’s daily lives, in which everyone could easily access our bubble, which means that existing sufferers of depression, who can’t seek medical help due to stigma, can obtain this sweet, delicious drink with a bubble that contains our engineered bacteria to help cure depression by producing taurine.
The biggest challenge to Menbles, our bubble, is the digestion of food in the stomach. Because most food coming from our mouth is digested in the stomach by the presence of a very strong acid called gastric acid, Menbles must be ensured to withstand the conditions in our stomach, due to our product’s aim to release the bacteria in the intestine, where our bacteria is supposed to produce taurine and then transported to the brain via the gut-brain axis. Luckily, sodium alginate is able to withstand these extreme conditions in the stomach. Sodium alginate itself, has been proven to have very little effect on itself when under extreme stomach conditions[1]. Therefore, we believe that it is a perfect solution for our case, for it to encapsulate our bacteria and not release it until reaching the intestine, where combined action of acid and trypsin can break the structure of alginate down[1], releasing the bacteria.
However, another challenge we encountered is that although alginate performs very well under acidic conditions, it does not, however, perform too well under basic conditions[2]. Therefore, we tested our bubbles containing E. coli Nissle 1917 to be submerged into phosphate buffers of four different pHs, reflecting the range of pHs of the milk tea drink. We also tested different bubble sizes to reflect the difficulty of swallowing among patients with mental illnesses[3], which themselves cannot chew our bubble to prevent the early release of bacteria. Because of this, we are interested to make our bubble as small as possible, so that these people will not feel the bubble as they are being swallowed. As a result, we also conducted experiments using different sizes of bubbles to identify which bubble size has the most stable recovery rate that we can use for our final product. Below are the results of the rate of recovery of our bubble for the 14.14 mm3 (Large) bubble, 4.19 mm3 (Medium) bubble, and 1.77 mm3 (Small) bubble (Fig. 2). For more detailed information, please refer to the Results page.
After analyzing our results (Fig. 2), the best size of bubble that has the most stable recovery rate among the different pHs of the milk tea drink, compared with other bubble sizes, is the 4.19 mm3 (Medium) bubble (Fig. 2). Therefore, this is the bubble size that we will expect to use for our final product, Menbles. After understanding the production of bubbles and overcoming the challenges to the digestion of our bubble, we will move on to what happens after the release of bacteria in the intestine.
Microfluidic Device
After we consume the engineered E. coli Nissle bubbles, the number of probiotics actually remaining in the human body is always confusing us. As a result, we intended to take the retention rate of E. coli Nissle in the jejunum into consideration. Nevertheless, due to the restriction of human trials and ethical issues, we came up with an idea to produce f(int) - a microfluidic channel to simulate the jejunum environment.

In our Generation 1 experimental results , as shown in Fig. 4, we found that the retention rate of microfluidic chip w/ CF+2villi is higher than any other channel. In addition, when we compare the result of the same channel with additional 5% HA (Hyaluronic acid) that will be the substitution of mucus, the retention rate increases by 5.45%.

The approach that we took to use 5% HA is because jejunum intestinal juice has 0.2 to 5% mucin(MUC2)[4], and HA was used because of its same sticky characteristic with mucin and due to its low availability. Our experiment result shows that the microfluidic channel with a complex structure such as channel w/ CF+2villi that includes additional HA is the most suitable for simulating the human intestine.
Taurine Production Experiments
Oxidative Stress Sensing System Experiments
After confirming that most of the engineered bacteria can adhere to the walls of the intestine, we must prove that the bacteria can produce taurine. We designed our engineered bacteria to produce these enzymes only when the body is under high-stress levels, which are signaled by high levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and IFN-γ. The following experiments were performed to confirm that both oxidative stress and IFN-γ sensing systems can effectively detect their respective stress biomarkers and initiate taurine production.
The oxidative stress sensing system regulates the production of L-cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase (CSAD). It consists of the soxR gene (BBa_K3771100), promoter PsoxS (BBa_K3771048), and the csad gene (BBa_K3771008). When SoxR protein is fully oxidized, it becomes a powerful transcription activator of PsoxS, leading to the expression of the downstream gene. To test the intensity and specificity of the oxidative stress sensing system, the oxidative stress assay was performed.
Oxidative Stress Assay
Achievements
1. Compared the intensity and sensitivity of different promoters under the stimulation by oxidative stress.
2. Selected a suitable promoter for regulating the expression of L-cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase (CSAD).
Process
We compared the relative fluorescence intensity of sfGFP expressed by different promoters when induced by different concentrations of paraquat (PQ). Paraquat can react with oxygen to produce various types of reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as superoxide radical (O2−•), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radical (OH−•)[5], which is used to simulate abnormal oxidative stress in the intestines of stressed individuals.
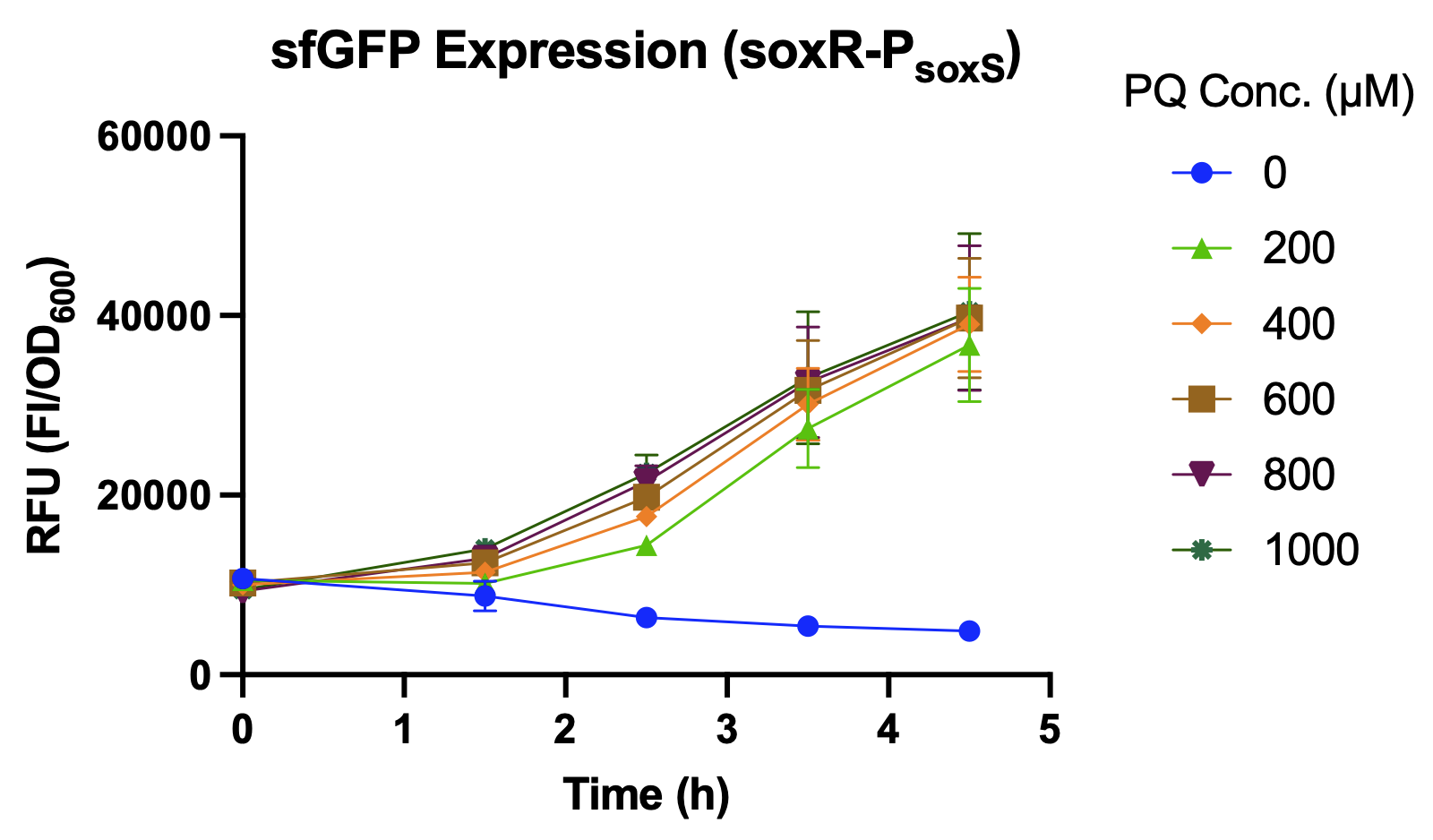
Over a period of 4.5 hours after paraquat was added, the relative fluorescence intensity was measured. J23100, a constitutive promoter, being the positive control, shows no difference in sfGFP expression level between the samples with and without paraquat. The activity of PsoxS (BBa_K3771048) is higher than that of PkatG (BBa_K3771047), but the activity is greatest when the SoxR transcription factor (BBa_K3771100) is added in the construction together with PsoxS (Fig. 6).
Another oxidative stress assay was performed only with SoxR and PsoxS promoter to determine the efficiency of this detection system. The sfGFP level was measured hourly during the 4.5 hours after paraquat induction, and results showed that even low concentrations of paraquat were able to activate the detection system (Fig. 8 and 9).
Interferon-gamma Sensing System Experiments
The second detection system is the IFN-γ sensing system, which regulates the production of CS.
The pathway for the IFN-γ sensing system requires two steps. First, ompA promoter constitutively expresses the OmpA/OprF chimeric protein, which is located in the plasma membrane of E. coli. Then, IFN-γ binds to the chimeric protein, activating a series of signal transduction reactions and finally inducing the pspA promoter and producing the CS enzyme. An IFN-γ induction assay was performed to confirm the function of the IFN-γ sensing system.
IFN-γ Induction Assay
Achievements
1. Selected a suitable promoter for regulating the expression of chimeric OmpA/OprF protein
2. Determined the minimum IFN-γ concentration required for activation of the sensing system
3. Determined the time required for the system to produce a significant difference in protein expression
Process
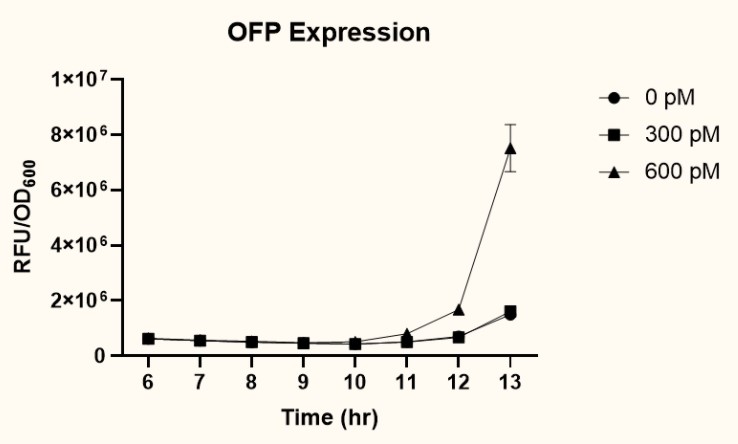
The two plasmids PpspA-ofp-PlacI-ompA/oprF (BBa_K3771017) and PpspA-ofp-PompA-ompA/oprF (BBa_K3771018) were transformed into ompA gene knockout strain, JW0940, to prevent OmpA from interfering with IFN-γ binding to chimeric OmpA/OprF. Human IFN-γ of concentrations 300 pM and 600 pM were added to bacteria cultures to induce the system. OFP expression (RFU) was recorded using a microplate reader and normalized by OD600. As shown in Fig. 11 and 12, starting at around 12 hours after induction, OFP expression of both samples increased dramatically.
As presented in Fig. 13, at 12 hours after induction, sample 2 (PpspA-ofp-PompA-ompA/oprF) (BBa_K3771018) with the addition of 600 pM IFN-γ had higher OFP expression than that of sample 1 (PpspA-ofp-PlacI-ompA/oprF) (BBa_K3771017). Since ompA promoter stimulates higher protein expression than lacI promoter, we decided to incorporate the ompA promoter in our final biobrick to regulate the expression of cs.
Model
Since reducing the amount of ROS was the main goal of Menbles, the mechanism we proposed was the anti-oxidative characteristic of the taurine derivative, TauCl. TauCl could induce lots of antioxidants to be produced within the intestinal epithelial cell. We modeled how GSH, one of the main antioxidants, could relieve ROS (see Fig. 14) in a faster and stronger way. Followed by the physiological mechanism proposed in Description a healthy gut could bi-directionally influence the brain, ultimately reducing various depressive symptoms.
References
- Guo L, Goff HD, Xu F, et al. The effect of sodium alginate on nutrient digestion and metabolic responses during both in vitro and in vivo digestion process. Food Hydrocolloids. 2020;107:105304. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105304
- Chuang J-J, Huang Y-Y, Lo S-H, et al. Effects of pH on the Shape of Alginate Particles and Its Release Behavior. International Journal of Polymer Science. 2017;2017:1-9. doi:10.1155/2017/3902704
- Aldridge KJ, Taylor NF. Dysphagia is a Common and Serious Problem for Adults with Mental Illness: A Systematic Review. Dysphagia. 2011;27(1):124-137. doi:10.1007/s00455-011-9378-5
- Leal J, Smyth HDC, Ghosh D. Physicochemical properties of mucus and their impact on transmucsal drug delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2017;532(1):555-572. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.09.018
- Lascano R, Muñoz N, Robert G, Rodriguez M, Melchiorre M, Trippi V, et al. Paraquat: an oxidative stress inducer. In: Mohammed Nagib Hasaneen, editors. Herbicides—Properties, Synthesis and Control of Weeds. Shanghai: In TechChina. 2012. Pp135–148.