Engineering
Introduction
In modern society, more and more people suffer from mild or severe depression. It
has been reported that malondialdehyde (MDA) level in the plasma of depressed patients is significantly
increased. After receiving conventional antidepressant treatment, the patient's MDA level decreased to the
same as that of healthy people. Therefore, researchers believe that oxidative stress may play an important
role in the occurrence and development of depression, and the activity of antidepressant therapy may be
mediated by improving oxidative stress/antioxidant function. We attempt to express an antioxidant enzyme
system (peroxidase gene efeB) in the cell or on the surface of the engineered probiotic bacteria to inhibit
the production of malondialdehyde (MDA) by human cells and prevent cell oxidation from causing health damage
to the body. So as to prevent or alleviate the condition of depression.
Design
The oxidation rate of peroxisome increases in proportion to the increase of oxygen
tension. Especially in the case of high oxygen concentrations, the oxidation reaction of peroxisomes
dominates. This characteristic allows peroxisomes to protect cells from the toxic effects of high
concentrations of oxygen. efeB reduces the oxidative stress in the cell by competing with mitochondria for
oxygen, and reduces the MDA produced during the oxidation of lipids.
 Figure 1. Action and function of efeB in MDA reduction.
Figure 1. Action and function of efeB in MDA reduction.
Build
Four recombinant plasmids were constructed (plasmid A:pUC57-Pro-efeB; plasmid
B:pUC57-amilGFP; plasmid C:pUC57-Pro-efeB-amilGFP) (Figure 1). Plasmid A is used to produce recombinant efeB
in probiotic bacteria. Plasmids B and C are used to confirm function of the composite part and expression of
efeB, respectively. All the constructs are confirmed by DNA sequencing.
 Figure 1. Schematic map of plasmids.
Figure 1. Schematic map of plasmids.
Test
Bacteria A (contains plasmid A, pUC57-efeB), and the bacteria D (contains plasmid
D, pUC57 empty vector). Bacteria A, which produces efeB enzyme, can survive in high concentration of
hydrogen peroxide (Figure 2).
 Figure 2. Histogram of relative biomass of bacteria A and B against different concentrations of
H2O2.
Figure 2. Histogram of relative biomass of bacteria A and B against different concentrations of
H2O2.
Bacteria A and C kept the MDA concentration dramatically lower than those of
Bacteria D (transformed with pUC57 vector) under the hydrogen peroxide concentration of 0mM, 2mM and 2.5mM.
Bacteria A and C with the efeB gene all effectively reduced the MDA concentration to the level lower than
Bacteria D (Figure 3).
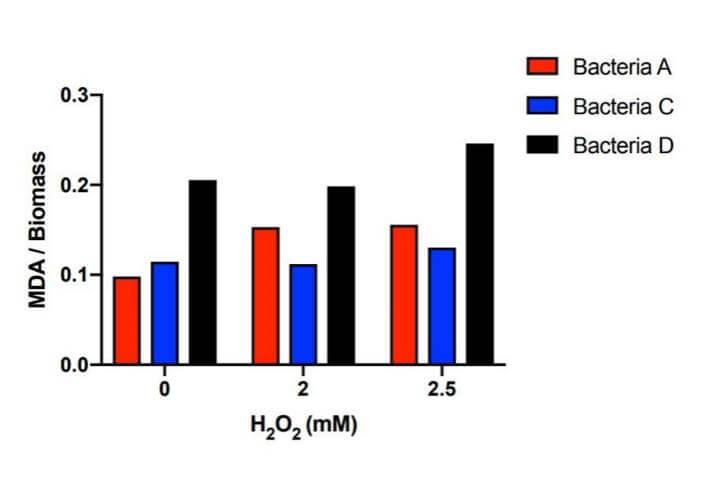 Figure 3. Histogram of MDA in the systems with different H2O2 concentration.
Figure 3. Histogram of MDA in the systems with different H2O2 concentration.
Learn
This shows that bacteria with the efeB gene is able to survive when the level of
ROS increases. As the concentration of hydrogen peroxide increases to 4mM, the relative biomass of both
bacteria A and bacteria D are zero. This shows that when the level of ROS is too high, bacteria are unable
to survive regardless of the presence of the efeB gene. Bacteria with the efeB gene effectively reduced the
MDA concentration to the lower level. Our genetically engineered bacteria are promising in preventing or
alleviating the condition of depression.
