
Overview
The implementation of our project is divided into three steps.

Figure1. The flow of implementation
Laboratory realization
The first step is to use synthetic biology technology to realize gene pathways in our iGEM laboratory.
We have extensively consult the literature related to papermaking and deinking, learn about the existing difficulties and problems in deinking. Finally, we determine the technical route of our project. We strive to miniaturize, homeize
and facilitate the deinking equipment. Our idea is that the generated waste paper will be treated in situ with convenient deinking equipment and new paper will be generated for office use. The whole process is convenient, fast and
environmentally friendly.
The idea of our project was to use synthetic biology, a variety of bioenzymes produced by Pichia pastoris, and hardware facilities with high intelligence and efficiency to complete the in-situ regeneration of paper. At present, we have
successfully expressed cellulase and xylanase that can be used for deinking in the laboratory and verified their function . Click here for more information

Figure2. The gene pathway we designed
At the same time, we also use market research to find our target users and markets, and analyze existing needs that are not met by existing solutions. This provides us with the direction of project realization and development. We carried
out a series of market researches at the beginning of the project. Our interviewees include college students, office staff of enterprises and institutions, government department employees, primary and secondary school students, teachers,
self-employed private owners and freelancers. They come from 25 provinces, cities and regions in China, covering from children a few years old to pensioners in their 60s and 70s. The content of the survey includes but is not limited
to the current situation of paper use, the acceptance of paper quality loss after deinking, deinking effect, effluent treatment and psychological price, etc. Now we have deeply understood the needs of paper and deinking equipment from
different groups, and analyzed their needs' differences between people, so as to continuously modify and improve our project itself. Click here for more information

Figure3. The survey related to paper deinking
Theoretical Realization
The second step is the possibility of theoretical realization of our project under existing conditions.
Through theoretical modeling, big data analysis and machine learning, the feasibility and innovation of our scheme have been preliminarily proved. The analysis of market risks enables us to respond positively to constant changes in the
market.
Counting the amount of residual ink on waste paper intelligently and accurately has always been a difficult point for deinking equipment to achieve. Through a large number of ink point deinking experiments on the paper, we verified the
spatial distribution of ink points by t-test and non-parametric inspection. Then we designed an ink point recognition algorithm suitable for our equipment using the obtained data. Accurate recognition and deinking of ink points makes
the deinking process more intelligent and accurate. Click here for more information
In order to make our deinking equipment more marketable, we want to combine the deployment of deinking machines with the needs of urban office paper. Imagine that if the deinking equipment is deployed to hospitals, schools, government
agencies, enterprises and institutions, users will be more willing to use it. We have established relevant mathematical models using the map of a large city in China, which provides an important reference value for the final launch
of our deinking equipment. When the spatial structure of the city is related to people's needs, modeling enables us to deliver deinking equipment more accurately. Click here for more information
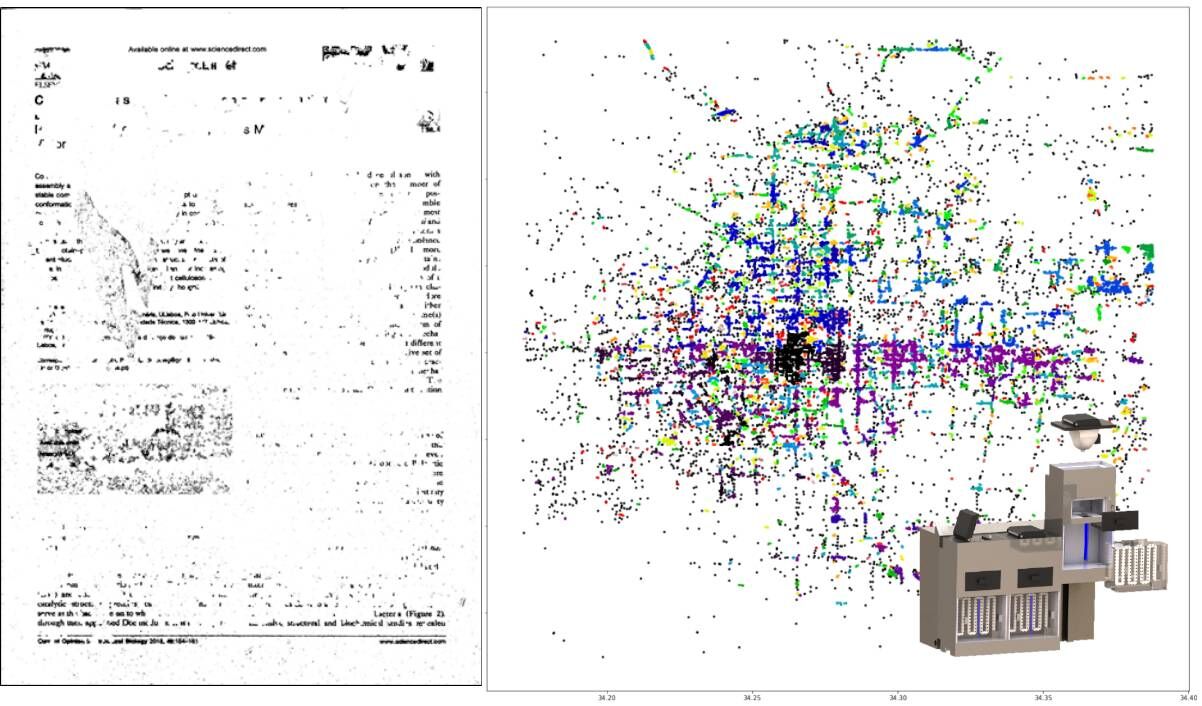
Figure4. The model based on deinking requirements
The road to commercialization is accompanied by challenges and risks. We analyzed the risks we may face from market, technology, product quality, operation, finance and users. On this basis, we consulted professionals to formulate a reasonable
response strategy. These strategies enable us to meet the challenges and risks calmly in entrepreneurship in the near future. Click here for more information
Practice and Entrepreneurship
The third step is practice and entrepreneurship.
Any emerging thing has a long way to go from theory to reality. We have put forward practical products, analyzed the risks, opportunities and challenges in the process of starting a business, and finally formulated a complete plan on how
to realize the product.
We carefully prepared business plans, participated in innovation and entrepreneurship competitions, and simulated business road shows. Now we are still on the way: We debated passionately in the Sino-US Maker Contest in Chengdu; We held
a roadshow on the stage of the Zhongguancun Talent Maker Competition in Beijing; We put our products and ideas on display in Chengdu International Environmental Expo. Click here for more information

Figure5. Giving an oral defense in Zhongguancun Talent Maker Contest

Figure6. Active communication in Sino-US Maker Competition
Our project starts at iGEM but not limited to iGEM. Our project is based on the principles of synthetic biology but oriented towards practical significance. Throughout the implementation of the project, we carried out rich and meaningful
human practice activities around deinking, waste paper recycling and synthetic biology. On the one hand, we have studied advanced environmental protection concepts of waste paper recycling from a number of recycling stations, paper
factories and key national laboratories. On the other hand, we spread these concepts to a wider range of people in science and technology museums, on university campuses and the Internet. This injects more meaning and connotation into
our project. As we originally imagined, we hope that a simple deinking device can enter every household to promote green environmental protection further.

